Electric buses are growing in numbers in Sweden, which contributes to the development of a fos- sil fuel free society and areduction of emissions. Earlier studies of bus systems have identified a need to further investigate societal costs, total cost of ownership, energy use on a yearly basis to account for seasonal variations, and noise during acceleration. Addressing those needs was the purpose of this study.
Investigations were made in five cities in Sweden that have recently implemented different electric buses in their respective public transport system. Based on results from these investigations and earlier studies, new and developed models where designed and applied on electric buses on route 1 in Karlskrona, as a representative example. It was found that there were significant savings in societal costs and total cost of ownership when compared to diesel and biogas powered buses, mainly due to decreased noise, no emissions in the use phase, and decreased energy use.
This paper used experiences from previous studies by Nurhadi, Borén & Ny (2014) and Borén & Ny (2016) about electric buses within the SustainTrans team and the GreenCharge project, and added new findings from the electric bus project that was funded by the Swedish Energy Agency. The results where found in cooperation with partners from Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborgs Energi, Electrodriving Scandinavia, Nobina, Karlstadsbuss, Keolis, Skånetrafiken, Volvo Buses, and Svealandstrafiken AB. Västmanlands lokaltrafik AB also provided great help during the noise measurements in Västerås, as well as the city planning department at Karlskrona Municipality with data for calculating societal costs from noise and the Swedish Transport Administration for support with conceptual noise calculations.
Published (open access) as: Borén, S. (2019). Electric buses’ sustainability effects, noise, energy use, and costs. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 10(3), 1–16. http://doi.org/10.1080/15568318.2019.1666324
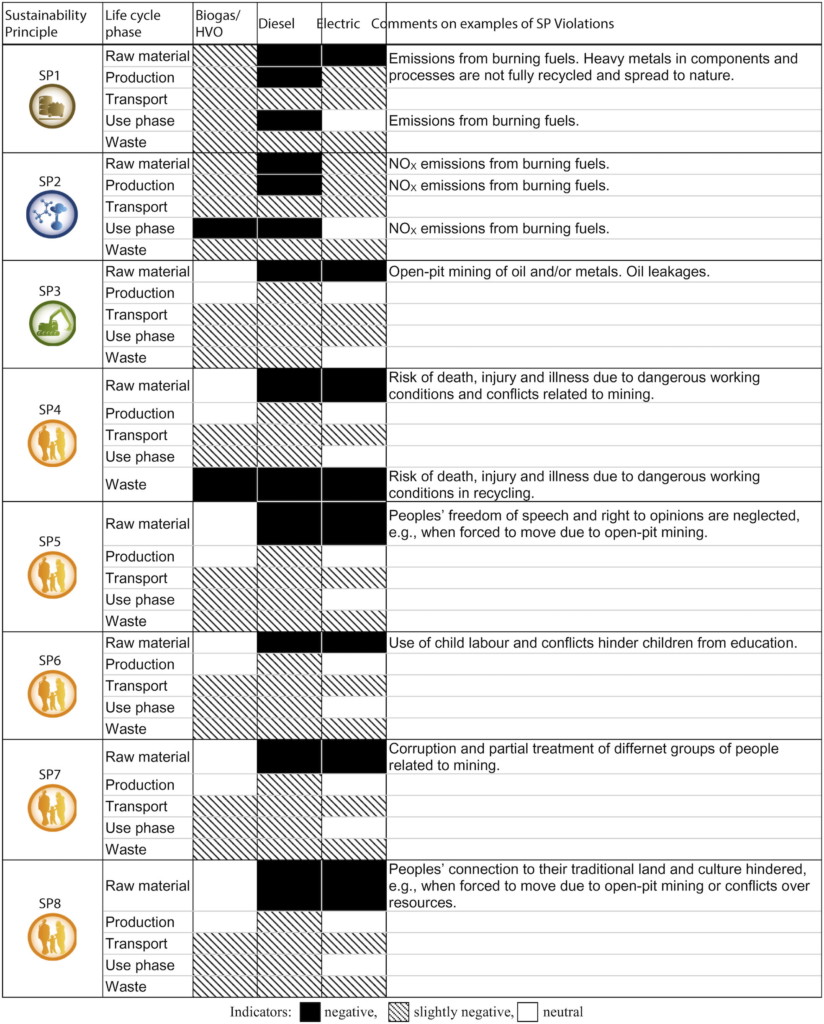
Strategic Life Cycle Assessment of buses powered by different energy carriers.
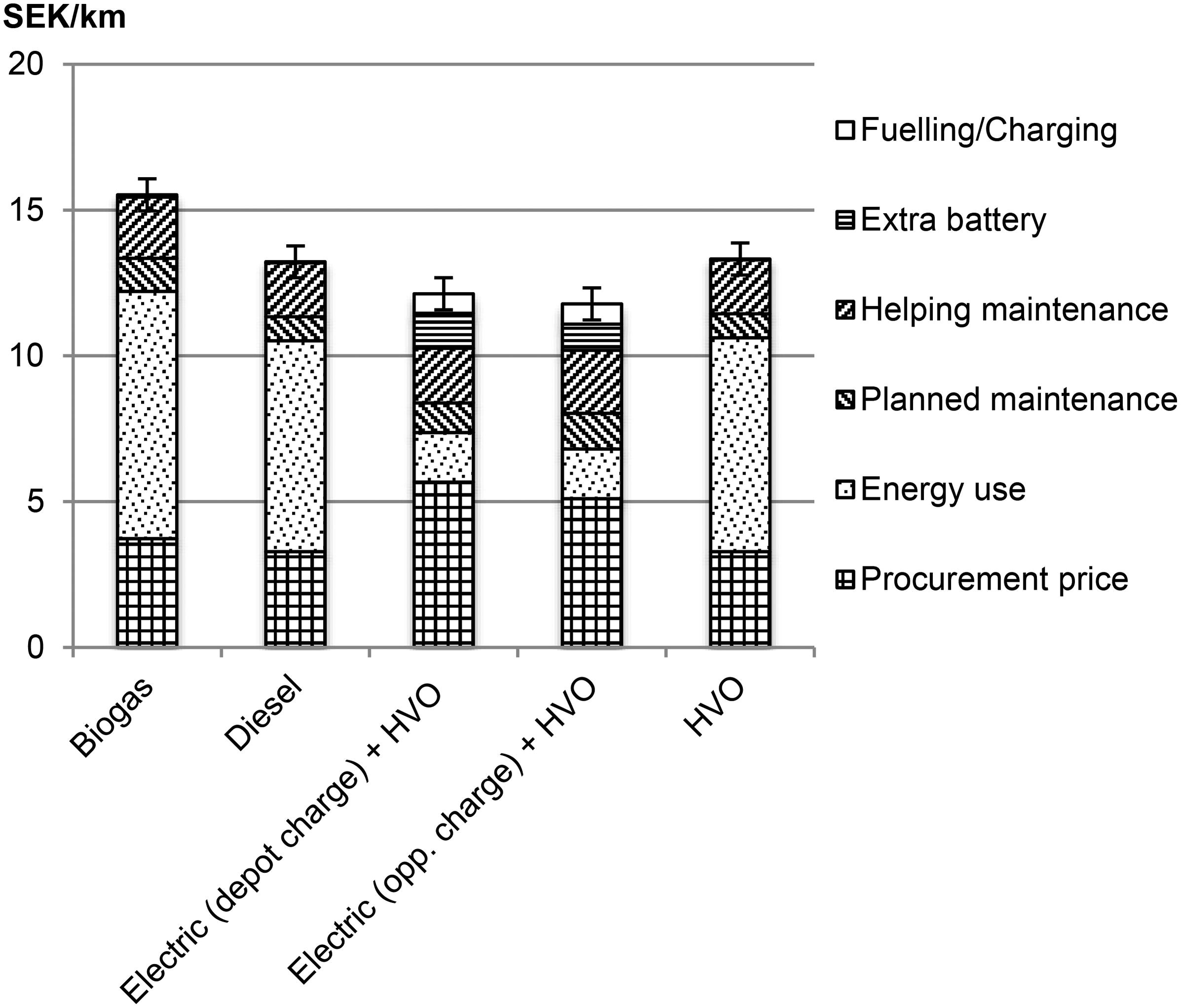
Total cost of ownership for buses powered by Biogas, Diesel, Electricity (opportunity charging), Electricity (depot charging), and HVO.
